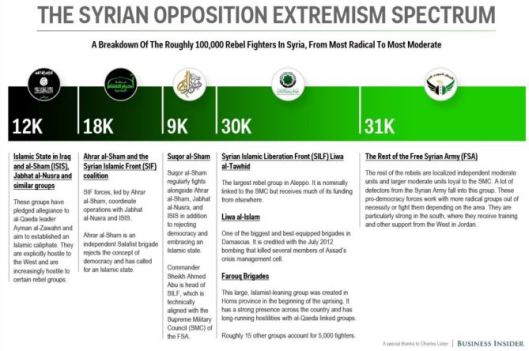
In my earlier articles – see appendix on the end – I claimed that there’s little dispute that a chemical agent was used in an Aug. 21st 2013 attack outside of Damascus – and probably on a smaller scale before that – but there is a reasonable doubt if the Assad regime used sarin gas in this operation. The CW attack nearly led to U.S. military intervention against Syria. From my perspective this case should not be forgotten as it is a good example about media war and can be repeared as e.g. as false flag operation in other theatres.
It might be possible that US did not implemented planned military intervention against Syria as its political leadership knew first that Syrian rebels had chemical weapons, second it knew that Al Assad regime maybe not used CW in Damascus August 2013 and third that Syrian opposition might on the end not be better alternative than Al Assad.
However now Prof. Tim Andersson his comprehensive analysis – Chemical Fabrications: East Ghouta and Syria’s Missing Children – reblogged here below:

The dirty war on Syria has involved repeated scandals, often fabricated against the Syrian Government to help create pretexts for deeper intervention. Perhaps the most notorious was the East Ghouta incident of August 2013, where pictures of dead or drugged children were uploaded from an Islamist-held agricultural area east of Damascus, with the claim that the Syrian Government had used chemical weapons to murder hundreds of innocents. The incident generated such attention that direct US intervention was only averted by a Russian diplomatic initiative. The Syrian Government agreed to eliminate its entire stockpile of chemical weapons (Smith-Spark and Cohen 2013), maintaining that it had never used them in the recent conflict.
Indeed, all the independence evident on the East Ghouta incident (including evidence from the US and the UN) shows that the Syrian Government was falsely accused. This followed a series of other false accusations, ‘false flag’ claims recorded by senior nun Mother Agnes (SANA 2011), a shamefully biased investigation into the Houla massacre (see Anderson 2015) and failed or exposed attempts to blame the Syrian Government over Islamist group killings, for example at Daraya and Aqrab (Fisk 2012; Thompson 2012). The Islamist groups’ use of chemical weapons was mostly dismissed by the western powers, and that dismissal has been reflected in most western media reports. However, because the chemical weapon claims have been repeated for years, public perceptions seem to have little reference to facts based on evidence. After a little background, let’s consider the independent evidence on the East Ghouta incident, in some detail. Arising from that evidence we are led to another serious crime of war, the fate of the dead or drugged children portrayed in those infamous images.
1. Chemical Weapons in Syria
Chemical weapons are a crude relic of an earlier era, such as the trench warfare of a century ago. They have no utility in urban warfare, where an army hunts armed groups amongst streets, buildings and civilian populations. No real utility, unless a ruthless party wants to create a general panic. In the case of the Syrian Arab Army, their conventional weapons were far superior to such crude weapons and their urban warfare training, often done in Iran, had the aim of rooting out terrorist groups, building by building (al Akhras 2013). A stockpile of chemical weapons had been kept as a deterrent to Israel, which holds nuclear weapons; but there had been no proven use of them in recent decades.
By mid 2013 the war had turned in favour of the Government. Although parts of Aleppo and some parts of eastern Syria were held by various Islamist groups, the Army had secured the major populated areas in western Syria and had closed much of the armed traffic across the mountainous Lebanese border. Along the borders with states which backed the Islamists – Turkey, Israel and Jordan – there were regular incursions, but they were always beaten back by the Syrian Army. Over May-June 2013 the Army, backed by Lebanon’s Hezbollah militia, took back the city of Qusayr, south-west of Homs, from a combination of the Farouq Brigade and Jabhat al Nusra, including many foreigners (Mortada 2013).
In this context anti-government armed Islamist groups were accused of using chemical weapons. The main foreign support group for the Syrian Islamists, Jabhat al Nusra, were reported to have seized a chemical factory near Aleppo in December 2012 (Gerard Direct 2012). Then in March the Syrian Government complained to the UN that sarin gas had been used in a major battle with the Islamists at Khan al Assal, west of Aleppo. The Syrian news agency SANA reported that terrorists had fired a rocket ‘containing chemical materials’, killing 16 people and wounding 86, soldiers and civilians. The death toll later rose to 25 (Barnard 2013). The Muslim Brotherhood-aligned British-based source, the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, along with other anti-government ‘activists’, confirmed the casualties but insinuated that the Syrian Army might have used the weapons and ‘accidentally’ hit themselves (Barnard 2013). Western media reports mostly elevated the Islamist counter-claims to the level of the Government’s report. In April 2013 Jabhat al Nusra was reported as having gained access to chlorine gas (NTI 2013).
About Khan al Asal, a 19 March statement from Syria’s UN Ambassador, Bashar al Ja’afari, said that ‘armed terrorist groups had fired a rocket from the Kfar De’il area towards Khan Al Asal (Aleppo district) … a thick cloud of smoke had left unconscious anyone who had inhaled it. The incident reportedly resulted in the deaths of 25 people and injured more than 110 civilians and soldiers who were taken to hospitals in Aleppo’. The following day the Syrian Government ‘requested the Secretary-General to establish a specialized, impartial independent mission to investigate the alleged incident’ (UNMIAUCWSAA 2013: 2-3).
Almost immediately following this, from 21 March onwards, the governments of the USA, France and Britain (all of which were by then directly or indirectly supporting the Islamist groups) began to add a series of incidents, claiming the use of chemical weapons in Syria (UNMIAUCWSAA 2013: 2-6). Washington repeatedly claimed there was ‘no proof’ the ‘rebels’ were responsible for chemical weapon use. They sought to turn the accusations against the Syrian Government.
However, in an interim statement in May, UN investigator Carla del Ponte said she had testimony from victims that ‘rebels’ had used sarin gas (BBC 2013). Then in May, Turkish security forces were reported to have found a 2kg canister of sarin, after raiding the homes of Jabhat al Nusra fighters (RT 2013). In July Russia announced it had evidence that Syrian ‘rebels’ were making their own sarin gas (Al Jazeera 2013).
Despite dissatisfaction over the Houla inquiry the previous year (see Anderson 2015), the Syrian Government invited UN inspectors to visit the Khan al Asal attack site. Details were organised and the UN’s Special Mission finally arrived in Damascus on 18 August 2013. The Mission ‘intended to contemporaneously investigate the reported allegations of the use of chemical weapons in Khan Al Asal, Saraqueb and Sheik Maqsood’, that is three of the 16 reported sites, ‘which were deemed credible’. However, ‘after the tragic events of 21 August 2013’ the UN Secretary General directed the group to investigate that incident ‘as a matter of priority’ (UNMIAUCWSAA 2013: 7-8). The East Ghouta incident and claims of mass gassing derailed the initially planned investigations. Despite the implausibility of the Syrian Government launching a chemical weapons attack, just as it had invited UN inspectors in Damascus, the Islamist claims succeeded in gaining world attention.
2. The East Ghouta Incident
The main armed Islamist group which controlled the area, the Saudi-backed Islamic Front (Liwa al Islam), blamed the Government for gassing children. Photos of dozens of dead or injured children were circulated. Supporting the ‘rebel’ accusations, the US government and the Washington-based Human Rights Watch blamed the Syrian government. Human Rights Watch said it had ‘analyzed witness accounts of the rocket attacks, information on the likely source of the attacks, the physical remnants of the weapon systems used’, and claimed the rockets used were ‘weapon systems known and documented to be only in the possession of, and used by, Syrian government armed forces’ (HRW 2013a). Much the same was said by the US Government. Close links between the two should tell us that this was more collaboration than corroboration. A group of Nobel Prize winners would later accuse Human Rights Watch of running a ‘revolving door’ between its offices and those of the US government (Pérez Esquivel, and Maguire 2014).
The New York Times backed the US Government claim ‘that only Syrian government forces had the ability to carry out such a strike’ (Gladstone and Chivers 2013). The paper claimed vector calculations of the rocket trajectories indicated they must have been fired from Syrian Army bases in Damascus (Parry 2013). Yet studies at MIT quickly showed the rockets to have a much shorter range than was suggested. The NYT retreated from its telemetry claims saying, while ‘some argued that it was still possible the government was responsible’, new evidence ‘undermined the Obama administration’s assertions’ about the rocket launch points’ (Chivers 2013; also Parry 2013). The final MIT report was more emphatic, concluding that the rockets ‘could not possibly have been fired at East Ghouta from the ‘heart’, or from the eastern edge, of the Syrian Government controlled area shown in the intelligence map published by the White House on August 30, 2013’ (Lloyd and Postol 2014).
While western media outlets mostly repeated Washington’s accusations, independent reports continued to contradict the story. Journalists Dale Gavlak and Yahya Ababneh reported direct interviews with ‘doctors, Ghouta residents, rebel fighters and their families’ in the East Ghouta area. Many believed that the Islamists had received chemical weapons via Saudi intelligence chief, Prince Bandar bin Sultan, and were responsible for carrying out the gas attack (Gavlak and Ababneh 2013). The father of a rebel said his son had asked ‘what I thought the weapons were that he had been asked to carry’. His son and 12 other rebels were ‘killed inside of a tunnel used to store weapons provided by a Saudi militant, known as Abu Ayesha’ (Gavlak and Ababneh 2013). A female fighter complained they had no instructions on how to use chemical weapons. A rebel leader said much the same. Many of those interviewed reported that their salaries came from the Saudi government (Gavlak and Ababneh 2013).
Next a Syrian group, ISTEAMS, led by Mother Agnes Mariam, carried out a detailed examination of the video evidence, noting that bodies had been manipulated for the images and that many of the children appeared ill or drugged (ISTEAMS 2013: 32-35). The videos used ‘artificial scenic treatment … there is a flagrant lack of real families in East Ghouta … so who are the children that are exposed in those videos? (ISTEAMS 2013: 44). All reports came from ‘rebel’ controlled areas. The medical office of the area claimed 10,000 injured and 1,466 killed, 67% of whom were women and children; while the Local Coordinating Committee (an FSA linked group) said there were 1,188 victims; but videos showed less than 500 bodies, by no means all dead (ISTEAMS 2013: 36-38). Even more striking was the subsequent absence of verified bodies. ‘Eight corpses are seen buried. [The] remaining 1,458 corpses, where are they? Where are the children?’ (ISTEAMS 2013: 41). A ‘rebel’ spokesperson claimed that ‘burials took place quickly for fear the bodies might decompose as a result of the heat’ (Mroue 2013).
The ISTEAMS report suggested a possible link with a large scale abduction of children in Ballouta, Northern Latakia, just two weeks prior to the East Ghouta incident. ‘We refer also the list of the victims of the invasion of 11 Alawite villages in Lattakia the 4th of August 2013, where 150 women and children were abducted by Jobhat Al Nosra’ (ISTEAMS 2013: 43). The report said: ‘the families of some adducted women and children … recognise their relatives in the videos’, and called for an ‘unbiased’ investigation to determine the identity and whereabouts of the children (ISTEAMS 2013: 44). Later reports noted that the children abducted in northern Syria had been held in the northern town of Selma (Martin 2014; Mesler 2014), with one alleging the armed groups had drugged those children to create a video, sending it to East Ghouta to be uploaded (Mesler 2014). If this were true, those children were never in the East Ghouta.
At the end of 2013 a Turkish lawyers and writers group issued a substantial report on crimes against civilians in Syria. A particular focus was the responsibility of the Turkish Government, which was backing the ‘rebel’ groups. The report concluded that ‘most of the crimes’ against Syrian civilians, including the East Ghouta attack, were committed by ‘armed rebel forces in Syria’. The Saudi backed group Liwa al Islam, led by Zahran Alloush, was said ‘by several sources to be the organization behind the chemical attack (Peace Association and Lawyers for Justice 2013).
North American veteran journalist Seymour Hersh interviewed intelligence agents and concluded that Washington’s claims on the evidence had been fabricated. Al Nusra ‘should have been a suspect’, he said, ‘but the [US] administration cherry picked intelligence to justify a strike against Assad’ (Hersh 2013). President Obama cited as evidence the Syrian Army’s preparation for a gas attack and ‘chatter’ on the Syrian airwaves at the time of the incident. However Hersh said he had found ‘intense concern’ and anger amongst agents over ‘the deliberate manipulation of intelligence’. One officer said the attack ‘was not the result of the current regime’ (Hersh 2013). The White House backgrounder combined facts after the event with those before. Hersh concludes that the White House ‘disregarded the available intelligence about al-Nusra’s potential access to sarin and continued to [wrongly] claim that the Assad government was in sole possession of chemical weapons’ (Hersh 2013).
The UN special mission on chemical weapons returned to Syria in late September and investigated several sites, including East Ghouta. They decided to investigate seven of the initial sixteen reports (UNMIAUCWSAA 2013: 10). This Mission was not briefed to determined responsibility, but rather to determine whether chemical weapons had been used and what had been the results. In a December 2013 report they reported that chemical weapons had been used in Syria, and specifically ‘against civilians, including children, on a relatively large scale in the Ghouta area of Damascus on 21 August … in Khan Al Asal on 19 March 2013 against soldiers and civilians … in Jobar on 24 August 2013 on a relatively small scale against soldiers … in Saraqueb on 24 August 2013 on a small scale, also against civilians … [and] in Ashrafiah Sahnaya on 25 August 2013 on a small scale against soldiers’ (UNMIAUCWSAA 2013: 19-21). Notice that on three of these five occasions chemical weapons were used against soldiers. Logically those attacks came from groups were fighting soldiers, not from government forces. A later report for the Human Rights Council (February 2014) noted that the chemical agents used in Khan-Al-Assal attack ‘bore the same unique hallmarks as those used in al Ghouta’; however they could not determine the perpetrator (HRC 2014: 19). The independent evidence was overwhelming and inescapable: chemical weapons had been used in East Ghouta, but the charges against the Syrian Army were fabricated.
| East Ghouta chemical weapons incident (August 2013): significant reports |
| Source/report/evidence |
Method and conclusion |
| Carla del Ponte (UN) |
Pre-East Ghouta: ‘Rebels’ believed to have used sarin gas in North Syria |
| Various news reports |
Pre-East Ghouta: ‘Rebels’ (al Nusra) arrested in Turkey with sarin gas |
| ‘Syrian Rebels’ and associates |
1,300+ killed, including children, from Government CW shelling (however only 8 bodies are publicly buried) |
| Human Rights Watch |
The CW used were only in possession of the SG |
| New York Times |
Telemetry evidence links attacks to SG bases (later MIT studies force NYT to modify this claim) |
| Lloyd and Postol (MIT) |
Rockets used had limited range and could not have been fired from suggested SG positions. |
| Gavlak and Ababneh (MINT Press) |
CW had been supplied by Saudis to ‘rebel’ groups, some locals had died due to mishandling |
| Mother Agnes / ISTEAMS |
Images were contrived, no social context, only eight people buried – who are the children? |
| John Mesler (NSNBC) |
Parents identified children in photos as those kidnapped in Latakia, two weeks earlier |
| Seymour Hersh (LRB) |
Interviewed US officials. Intelligence was manipulated to blame President Assad, false claims used. |
| Turkish lawyers and writers group (PALJ) |
Saudi backed ‘rebel’ group Liwa al Islam believed to be responsible. |
| UN Dec 2013 report on CW attacks in Syria |
CW were used in East Ghouta; three of five CW attacks were ‘against soldiers’ or ‘against soldiers and civilians’ |
| HRC Feb 2014 report |
chemical agents used in Khan-Al-Assal attack ‘bore the same unique hallmarks’ as those used in East Ghouta |
–
Independent evidence came from Syrian, Jordanian, Turkish and US sources, and from a United Nations team. Further, many of the displays of children were not reliably linked to East Ghouta. Nor is there independent verification of who those children are and what happened to them. The weight of evidence proves this was another ‘false flag’ incident, designed to attract deeper foreign intervention. The scale of independent reporting which undermines claims against the Syrian Government stands in contrast to the open self-publicity of ‘rebel’ atrocities such as beheadings, public executions, truck bombings, mortaring of cities, bombing of hospitals and destruction of mosques and churches. The fact that the Syrian Army strongly contests civilian atrocity claims (the treatment of captured fighters is another matter), while many of the ‘rebel’ groups publicise their own atrocities against civilians, sets a distinct background to these controversies.
3. Chemical Fabrications and Syria’s Missing Children
After the East Ghouta incident, Islamist groups supported by a range of anti-Syrian governments kept up their accusations, while covering up their own exposures. Jabhat al Nusra claimed the chemicals they were caught with in Turkey were ‘not for making sarin gas’ (Today’s Zaman 2013). Yet video evidence from south Syria showed al Nusra using chemical weapons against Syrian soldiers (Turbeville 2014). In July 2014 barrels containing sarin were reported as discovered in parts of ‘rebel-held Syria’ (RT 2014). Then in 2015 Iraqi Kurds reported the al-Nusra breakaway group ISIS using chemical weapons (Solomon 2015; Ariel 2015). Kurdish fighters seized chlorine canisters after a suicide bomb attack which left them ‘dizzy, nauseous and weak’ (Akbar 2015).
Anti-Syrian ‘activists’, plus US-based NGOs such as Avaaz, the Syria Campaign and The White Helmets, also repeated and extended their accusations, while urging a Libyan styled ‘no fly zone’ (NFZ Syria 2015; White Helmets 2015), clearly intended to topple the Government in Damascus. By 2014 there seemed little chance that would happen. Such one-sided campaigns seemed unlikely to do much except help extend the killings. In April 2014 Al Jazeera accused the Syrian Government of using chlorine gas (Baker 2014), while anonymous activists’ accused the Syrian army of a poison gas attack (Mroue and Lucas 2015). In neither case was there any independent verification. Counter-campaigners exposed the financial and political links between Washington and a range of US-based ‘civil society’ groups like Avaaz (Morningstar 2014; Sterling 2015). Nevertheless, media channels repeated the initial claims of the East Ghouta incident, as though they were fact, oblivious to the evidence. An April 2015 article in the UK Guardian, for example, claimed in its backgrounder that the Syrian Government had used chemical weapons and ‘killed up to 1,400 people in August 2013’ (Black 2015).
The smokescreens around chemical weapons have effectively derailed reasonable public discussion about the war in Syria, at least in western circles; and perhaps that was the point. It is sad, though, that reasonable discussion of the evidence should matter so little. Further, the constant stream of fabrications have certainly aggravated and helped prolong the violence. Islamist militia carry out their crimes with relative impunity, often blaming them on the Syrian Government.
Another crime has been buried by the chemical fabrications: the fate of the children kidnapped in Ballouta. Even Human Rights Watch reported this crime (HRW 2013b), if not the link to the children said to have been injured or killed in East Ghouta. This mass kidnapping was just one of many by the Islamist groups. The victims are held for ransom, for prisoner exchanges, or simply slaughtered because they are thought be from pro-government families. The latter was the case with Alawi families in the Aqrab massacre (Thompson 2012), while a failed prisoner exchange was behind the Daraya massacre (Fisk 2012).
However in the East Ghouta incident, several sources (ISTEAMS 2013; Martin 2014; Mesler 2014) now link the Ballouta children to the photos of the dead or drugged little bodies said to be in Ghouta. That is, their images may have been uploaded from East Ghouta but the bodies were never there. While some of those kidnapped were released in a 2014 prisoner exchange, many are still held; and this is said to be why many families in north Syria have not yet more publicly identified their children. The want to see them released. Western media sources continue refer to ’1,400′ dead, without names, but only eight bodies are known to have been buried. In the fog of war, Mother Agnes Mariam has been right all along to insist on names and details of people killed, and not just a recital of numbers, as though these killings were a cricket match. Back in September 2013 her ISTEAMS group posed one of the most most vital questions of this whole affair: ‘Eight corpses are seen buried’. [The] remaining 1,458 corpses, where are they? Where are the children?’ (ISTEAMS 2013: 41).
Notes:
Al Akhras, Samir (2013) Interview with this writer, Damascus, 24 December
Al Jazeera (2013) ‘Syria rebels made own sarin gas, says Russia’, 10 July, online: http://www.aljazeera.com/news/middleeast/2013/07/20137920448105510.html
Anderson, Tim (2015) ‘The Houla Massacre Revisited: “Official Truth” in the Dirty War on Syria’, Global Research, 24 March, online: http://www.globalresearch.ca/houla-revisited-official-truth-in-the-dirty-war-on-syria/5438441
Ariel, Ben (2015) ‘United States ‘concerned’ about ISIS use of chlorine gas’, Arutz Sheva, 17 March, online:http://www.israelnationalnews.com/News/News.aspx/192730#.VSJJc5MY6q4
Akbar, Jay (2015) ‘More evidence emerges of ISIS using chemical weapons as Kurdish fighters seize chlorine canisters after suicide bomb attack that left them ‘dizzy, nauseous and weak’’, 15 March, Daily Mail, online: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2995150/More-evidence-emerges-ISIS-using-chemical-weapons-Kurdish-fighters-seize-chlorine-canisters-suicide-bomb-attack-left-dizzy-nauseous-weak.html
Baker, Graeme (2014) ‘Syrian regime accused of chlorine gas attacks’, Al Jazeera, 17 April, online:http://www.aljazeera.com/news/middleeast/2014/04/syrian-regime-accused-chlorine-gas-attacks-201441703230338216.html
Barnard, Anne (2013) ‘Syria and Activists Trade Charges on Chemical Weapons’, New York Times, 19 March, online:http://www.nytimes.com/2013/03/20/world/middleeast/syria-developments.html?pagewanted=all
BBC (2013) UN’s Del Ponte says evidence Syria rebels ‘used sarin’’, 6 May, online: http://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-22424188
Black, Ian (2015) ‘Former ambassador attacks Cameron’s ‘arrogant’ Syria policy’, UK Guardian, 8 April, online:http://www.theguardian.com/politics/2015/apr/07/former-ambassador-attacks-camerons-arrogant-syria-policy
Chivers, C.J. (2013) ‘New Study Refines View of Sarin Attack in Syria’, New York Times, online: http://www.nytimes.com/2013/12/29/world/middleeast/new-study-refines-view-of-sarin-attack-in-syria.html
Eva Pal (2014) ‘Talk with Lilly Martin and Steven Sahiounie, part 1’, YouTube, May 10, online:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oc2HRk42O-w
Fisk, Robert (2012) ‘Inside Daraya – how a failed prisoner swap turned into a massacre’, 29 August:http://www.independent.co.uk/voices/commentators/fisk/robert-fisk-inside-daraya–how-a-failed-prisoner-swap-turned-into-a-massacre-8084727.html
Gavlak, Dale and Yahya Ababneh (2013) ‘Syrians In Ghouta Claim Saudi-Supplied Rebels Behind Chemical Attack’, MINT PRESS, August 29, online: http://www.mintpressnews.com/witnesses-of-gas-attack-say-saudis-supplied-rebels-with-chemical-weapons/168135/
Gerard Direct (2012) ‘Syria: jihadist al-Nusra Front seizes chemical factory near Aleppo’, 9 December, online:http://gerarddirect.com/2012/12/09/syria-jihadist-al-nusra-front-siezes-chemical-factory-in-allepo/
Gladstone, Rick and C.J Chivers (2013) ‘Forensic Details in U.N. Report Point to Assad’s Use of Gas’, New York Times, 16 September, online: http://www.nytimes.com/2013/09/17/world/europe/syria-united-nations.html?_r=0&adxnnl=1&adxnnlx=1387381766-55AjTxhuELAeFSCuukA7Og
Hersh, Seymour M. (2013) ‘Whose Sarin?’, London Review of Books, Vol. 35 No. 24, 19 December, 9-12, online:http://www.lrb.co.uk/v35/n24/seymour-m-hersh/whose-sarin
Hersh, Seymour M. (2014) ‘The Red Line and the Rat Line’, London Review of Books, 36:8, 17 April, pp 21-24, online:http://www.lrb.co.uk/v36/n08/seymour-m-hersh/the-red-line-and-the-rat-line
HRC (2014) ‘Report of the independent international commission of inquiry on the Syrian Arab Republic’, Human Rights Council, A/HRC/25/65, 12 February, online: http://www.ohchr.org/EN/HRBodies/HRC/IICISyria/Pages/IndependentInternationalCommission.aspx
HRW (2013a) ‘Attacks on Ghouta: Analysis of Alleged Use of Chemical Weapons in Syria’, Human Rights Watch, Washington,10 September, online: http://www.hrw.org/reports/2013/09/10/attacks-ghouta
HRW (2013b) ‘You Can Still See Their Blood’, Human Rights Watch, Washington, 11 October, online:http://www.hrw.org/node/119675/
ISTEAMS (2013) ‘Independent Investigation of Syria Chemical Attack Videos and Child Abductions’, 15 September, online:http://www.globalresearch.ca/STUDY_THE_VIDEOS_THAT_SPEAKS_ABOUT_CHEMICALS_BETA_VERSION.pdf
Lloyd, Richard and Theodore A. Postol (2014) ‘Possible Implications of Faulty US Technical Intelligence in the Damascus Nerve Agent Attack of August 21, 2013’, MIT, January 14, Washington DC, online: https://www.documentcloud.org/documents/1006045-possible-implications-of-bad-intelligence.html#storylink=relast
Malas, Nour (2013) ‘As Syrian Islamists Gain, It’s Rebel Against Rebel’, Wall Street Journal, 29 may, online:http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323975004578499100684326558.html
Martin, Lilly (2014) in Deena Stryker ‘The Hidden Australia/Syria Story’, Op Ed News, 22 December, online:http://www.opednews.com/articles/The-Hidden-Australia-Syria-by-Deena-Stryker-Children_Community_Death_Government-141222-294.html
Mesler, John (2014) ‘Combating the Propaganda Machine in Syria: The ‘Moderate Opposition’, the Children from Ballouta, and the Sarin Gas Attack on Eastern Ghouta’, NSNBC, 10 October, online: http://nsnbc.me/2014/10/10/combating-propaganda-machine-syria/
Morningstar, Cory (2014) ‘Syria, Avaaz, Purpose and the art of selling hate for empire’, Wrong Kinds of Green, 17 September, online: http://wrongkindofgreen.org/tag/white-helmets/
Mortada, Radwan (2012) ‘Syria Alternatives (II): no homegrown solutions’, Al Akhbar, 13 June, online: http://english.al-akhbar.com/content/syria-alternatives-ii-no-homegrown-solutions
Mortada, Radwan (2013) ‘The Battle for Qusayr: Decisive Victory or War of Attrition?’, Al Akhbar, May 21, online:http://english.al-akhbar.com/node/15864
Mroue, Bassem (2013) ‘Syrian forces bomb area of alleged chemical attack’ USA Today, 22 August, online:http://www.usatoday.com/story/news/world/2013/08/22/syria-attack/2683855/
Mroue, Bassem and Ryan Lucas (2015) ‘Activists accuse Syrian military of deadly poison gas attack’, 17 march, online:http://news.yahoo.com/group-syrian-attacks-may-amount-war-crimes-074128323.html
NFZ Syria (2015) ‘Call from Syria: London march 26th April’, 4 April, online: http://www.nfzsyria.org/
NTI (2013) ‘Syrian militants have access to chlorine gas: plant owner’, 1 April, online: http://www.nti.org/gsn/article/syrian-militants-have-access-chlorine-gas-plant-owner/
Parry, Robert (2013) ‘NYT Backs Off Its Syria-Sarin Analysis’, Global Research, 30 December, online:http://www.globalresearch.ca/nyt-backs-off-its-syria-sarin-analysis/5363023
Peace Association and Lawyers for Justice in Turkey (2013) ‘War Crimes Committed Against the People of Syria’, December, online: http://www.wpc-in.org/sites/default/files/documents/war-crimes-committed-againts-the-people-of-syria.pdf
RT (2013) ‘Turkey finds sarin gas in homes of suspected Syrian Islamists – reports’, 30 may, online: http://rt.com/news/sarin-gas-turkey-al-nusra-021/
RT (2014) ‘‘Abandoned’ barrels containing deadly sarin seized in rebel-held Syria’, 8 July, online: http://rt.com/news/171076-two-sarin-barrels-found-syria/
SANA (2011) ‘Mother Agnes Merriam al-Saleeb: Nameless Gunmen Possessing Advanced Firearms Terrorize Citizens and Security in Syria’, Syrian Free Press Network, 19 November, online: http://syrianfreepress.wordpress.com/2011/11/19/mother-agnes-merriam-al-saleeb-nameless-gunmen-possessing-advanced-firearms-terrorize-citizens-and-security-in-syria/
Smith-Spark, Laura and Tom Cohen (2013) ‘U.S., Russia agree to framework on Syria chemical weapons’, CNN, 15 September, online: http://edition.cnn.com/2013/09/14/politics/us-syria/
Solomon, Erica (2015) ‘Iraqi Kurds claim ISIS used chemical weapons’, Financial Times, 14 March, online:http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/6e69cfca-ca78-11e4-8973-00144feab7de.html#axzz3WW8sO2k1
Turbeville, Brandon (2014) ‘New video evidence points to al-Nusra chemical attack against Syrian soldiers’, 5 May, Online:http://www.activistpost.com/2014/05/new-video-evidence-points-to-al-nusra.html
Stack, Liam and Hania Mourtada (2012) ‘Members of Assad’s Sect Blamed in Syria Killings’, New York Times, December 12, online: http://www.nytimes.com/2012/12/13/world/middleeast/alawite-massacre-in-syria.html?_r=0
Sterling, Rick (2015) ‘Humanitarians for War on Libya’, Syrian Free Press, 5 April, online: https://syrianfreepress.wordpress.com/2015/04/05/report-44442/
Thompson, Alex (2012) ‘Was there a massacre in the Syrian town of Aqrab?’, 14 December: http://blogs.channel4.com/alex-thomsons-view/happened-syrian-town-aqrab/3426
Today’s Zaman (2013) ‘Detained al-Nusra members say chemicals not for making sarin gas’, 13 September, online:http://www.todayszaman.com/national_detained-al-nusra-members-say-chemicals-not-for-making-sarin-gas_326332.html
UN (2013) United Nations Mission to Investigate Allegations of the Use of Chemical Weapons in the Syrian Arab Republic, December, online: https://unoda-web.s3.amazonaws.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/report.pdf
UNMIAUCWSAA (2013) ‘Final report’, United Nations Mission to Investigate Allegations of the Use of Chemical Weapons in the Syrian Arab Republic, 12 December, online: https://unoda-web.s3.amazonaws.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/report.pdf
White Helmets (2015) ‘It’s time to stop the bombs’, March, online: https://www.whitehelmets.org/
o o o
Original article by Tim Anderson [GlobalResearch 12/4/2015]
o o o
Appendix: Some of my own articles about Syria:
Syria Updates: The New Islamic Front And Whodunnit III
Syria Chemical Weapons Attack – Whodunnit II
Demolition Of CW Stockpiles Is Only Contributory Factor In The Syria War
The Four-stage Plan For Syria – Can It Work
Whodunnit in Syria
Syrian Rebels Admit Chemical Attack In Damascus???
Syria: From War To Dissolution With Help Of Media
 Oil produced by the Islamic State group finances its bloodlust. But how is it extracted, transported and sold? Who is buying it, and how does it reach Israel?
Oil produced by the Islamic State group finances its bloodlust. But how is it extracted, transported and sold? Who is buying it, and how does it reach Israel? 



 Posted by Ariel Rusila
Posted by Ariel Rusila 




















 This
This
 Besides UN report there still are questions and observations unanswered rised in
Besides UN report there still are questions and observations unanswered rised in  O
O

 I
I